This guide explains how to use Zedmed to write a prescription and includes electronic prescribing (escripts), controlled medicines and authority approvals. There is also a Quickstart guide for eScripts.
Considerations
Prescribing Requirements:
- The patient requires a validated IHI in their patient record.
- The practitioner requires an HPI-I.
- The practitioner must have registered with eRx (erx.com.au) and have a unique eRx entity for each branch they work in.
- Enable Electronic Prescribing in Clinical > My Options > Drug Options.
Electronic prescribing - When a prescription is created, you can use ePrescribing to send a QR code for the prescription to the patient's mobile phone or email or to print the QR code. For the requirements and information, see ePrescribing with eRx.
My Health Record (MHR) - If a patient is registered for MHR, Zedmed's default settings will upload all prescriptions to MHR when you select Prescribe or Prescribe electronically. When the records have been uploaded, they will appear in the Summary Views tab and can also be viewed by opening My Health Record. To view the configurations available, see Setup My Health Record.
Controlled medicines - Zedmed provides an alert when a high-risk medicine is prescribed so the clinician can check the patient's prescription history. This solution uses the National Data Exchange (NDE) to provide Real-Time Prescription Monitoring (RTPM) via SafeScript in Victoria and NSW, QScript in Queensland and ScriptCheck in SA and WA.
Authority PBS prescriptions - Zedmed has a dedicated screen with the number to call for prescriptions that require Authority approval to be covered by PBS. The screen is also used for an Authority-required (STREAMLINED) prescription that does not require prior approval but does require the recording of a streamlined authority code.
Create a prescription
To create a printed or electronic prescription:
- Start an encounter with the patient.
For a detailed explanation of how to do this, see the Start an Encounter article.
When the encounter starts, the Current Encounter pane will open and display the clinical modules. - Select Drugs from the Current Encounter menu.
The first time a prescription is created for the patient, you will be prompted to record known allergies.
This will open the patient's Prescriptions screen with the current MIMS database of medications.
If MIMS needs updating, a yellow notification banner will appear on the top. To learn more, see the Update MIMS article.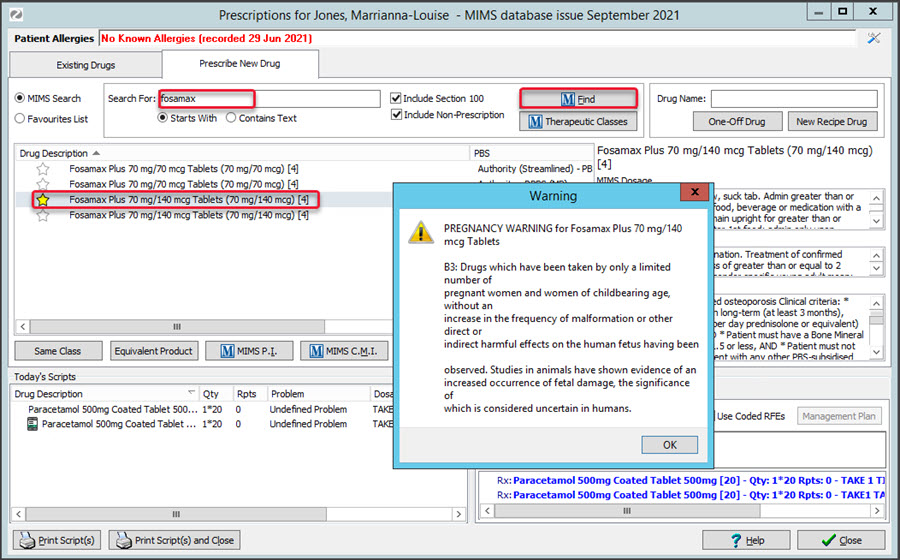
- Select the drug to prescribe.
To re-prescribe a drug:
a. Select the Existing Drugs tab.
This tab lists all medications that the patient is currently on.
b. Right-click the drug and select Re-prescribe Drug.
Selecting Prescribe New Strength searches for the medication and follows the prescribe a new drug process below.
To prescribe a new drug:- Select the Prescribe New Drug tab if it has not already been selected.
Generic drugs will appear with a blue G icon. Expanding a drug will reveal the non-generic option. - Enter the drug's name in the Search For field, select Find then double-click the drug in the search results.
OR - Double-click the drug from your Favourites List and go to step 6.
- Select the Prescribe New Drug tab if it has not already been selected.
- When you double-click the drug, you may be prompted to review the MIMs information then select Prescribe.
The Script Details screen will then open. This is where you enter the dosage instructions. These fields are pre-populated based on the drug selected. Not all of the information will be relevant, and there are no mandatory fields. - If the drug is a controlled medicine
If the prescription is for a controlled medicine, a real-time monitoring banner (e.g. Safescript) will appear.
• If the patient was not prescribed the drug elsewhere in the last six months, the banner will be green and stay for 3 seconds
• If the patient was prescribed the drug elsewhere in the last six months, the banner will be orange or red and stay open.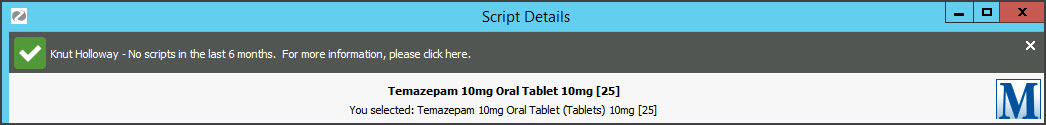
 Clicking the banner opens the RTPM portal so you can log in to look up the patient and perform a script history check. The portal will be SafeScript in Victoria and NSW, QScript in Queensland and ScriptCheck in South Australia.
Clicking the banner opens the RTPM portal so you can log in to look up the patient and perform a script history check. The portal will be SafeScript in Victoria and NSW, QScript in Queensland and ScriptCheck in South Australia. - Enter the dosage instructions for the patient using one of these methods:
• Use the Dosage Calculator, Frequency selector and Instructions selector to populate the dosage fields.
• Manually type the dosage instructions into the Dosage Full Text field.
• Copy instructions from the MIMS Dosage field. Highlight the text, right-click it and select Paste to Dosage.
Note: From March 31, 2023, Dosage Full Text is required for electronic prescriptions and requires Zedmed v36.5 or later.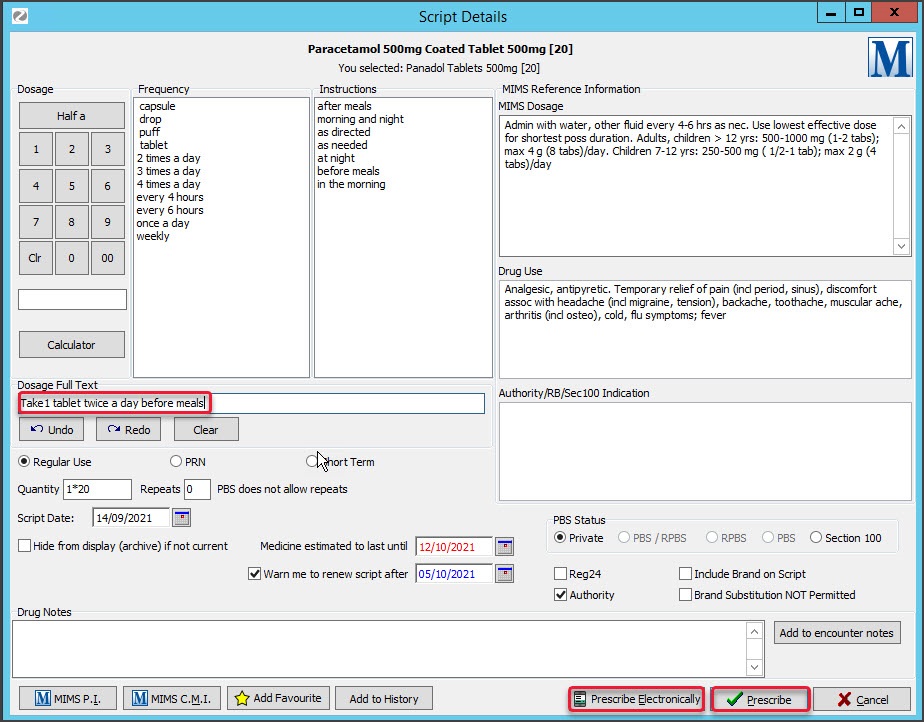
- Review the other information shown in the Script Details screen.
These fields are pre-populated based on the drug selected. Not all the information will be relevant, and there are no mandatory fields. To learn more, see the Script Details screen article.
Five key fields are:
- Add Favourite - adds the prescription to your favourites list with all the details you entered. This is useful for a drug that's frequently prescribed.
- Add to History - adds the prescription to the patient’s history. This is used to enter medications the patient is taking that were not prescribed by your practice.
- Authority - this box is ticked if the prescription requires Authority Approval for the PBS. The tick is to advise that Authority Approval will be prompted. Removing the tick will not stop the Authority Approval screen from opening,
- Reg24 - tick this box (if required) for a patient that is eligible for repeats under Reg24, and the text "Reg.24" will be added to the script. To learn more, see the government's Regulation 24 guidance.

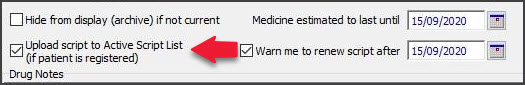
- Active Script List - The Upload script to Active Script List option appears if the patient has an active Active Script List (ASL). The box is selected by default, which means scripts submitted electronically, including paper-based ETP scripts and electronic prescriptions, will be added to the ASL. This function does not transfer any other patient information.
-
Select Prescribe Electronically (ePrescribing/escripts) for an electronic prescription.
OR
Select Prescribe for a printed prescription.Note: When you select Prescribe or Prescribe Electronically, Zedmed's default setting uploads prescriptions to My Health Record if the patient has not opted out.
-
Authority Approval
Proceed with one of the 3 options:
If the drug is covered by the PBS with Authority Approval, the Approval screen will open.
• Codes will be provided for drugs with a Streamlined Authority option. Choose the correct code, then select Authority.
• For drugs that require Authority approval, call the hotline to get the code to enter, then select Authority.
• If you select Private, the full cost of the drug will be charged to the patient.
To learn more, see the Authority Approval section below. -
Complete the prescription.
Prescribe (printed prescription)
If you select Prescribe from the Script Details screen, the screen will close, and the script will appear in Today's Scripts. Select the script then the Print Scripts icon to print it out.
Select the script then the Print Scripts icon to print it out.
From this screen, you can right-click the script and select Reprint.
Note: You cannot go back to the Today's script section on another day. You can only reprint the script on the same day. Once the day has ended, you need to do a re-prescribe to print a new script.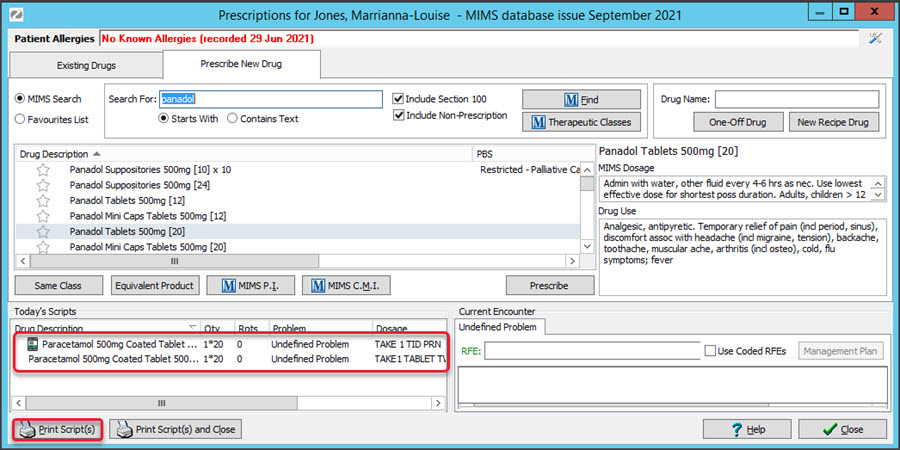
Prescribe Electronically (ePrescribing)
a) From the Script Details screen, select Prescribe Electronically
The Electronic Prescription screen will open. b) Review the fields on the Electronic Prescription screen.
b) Review the fields on the Electronic Prescription screen.
• Route of Administration & Clinical indication - use if there are different options available for the medication.
• Minimum Repeat Interval - used to specify how many days should pass before the patient can get a repeat.
• Warrant number/Permit number - when dispensing a schedule 4 medicine, enter the number required by your state.
VIC: Warrant no. | SA: Permit no. | QLD/ACT: Approval no. | WA/TAS: Authority no. | NSW/NT: Authorisation No.
• Unusual Dose - used to acknowledge that the dosage specified is not the standard dosage.
• Script is for urgent supply - used for a mediation that's been dispensed. This script is only sent to the pharmacy.
c) Select SMS or Email.
The SMS and Email fields contain the patient's mobile and email address. You can also manually enter the information.
d) Select the Prescribe Electronically button.
The ePrescribing QR code will be sent to the patient.
Option - No Electronic Token
Tick Print Paper Token to print out the prescription's QR code.
Option - Send directly to pharmacy
In Zedmed v36.5 and later, there is a Send directly to Pharmacy checkbox with a reasons field. This will print out a QR code (token) for the prescription that can be faxed or scanned and emailed directly to the pharmacy. This is for compliance with state and territory legislation that prevents prescriptions from being given to patients for specific controlled substances.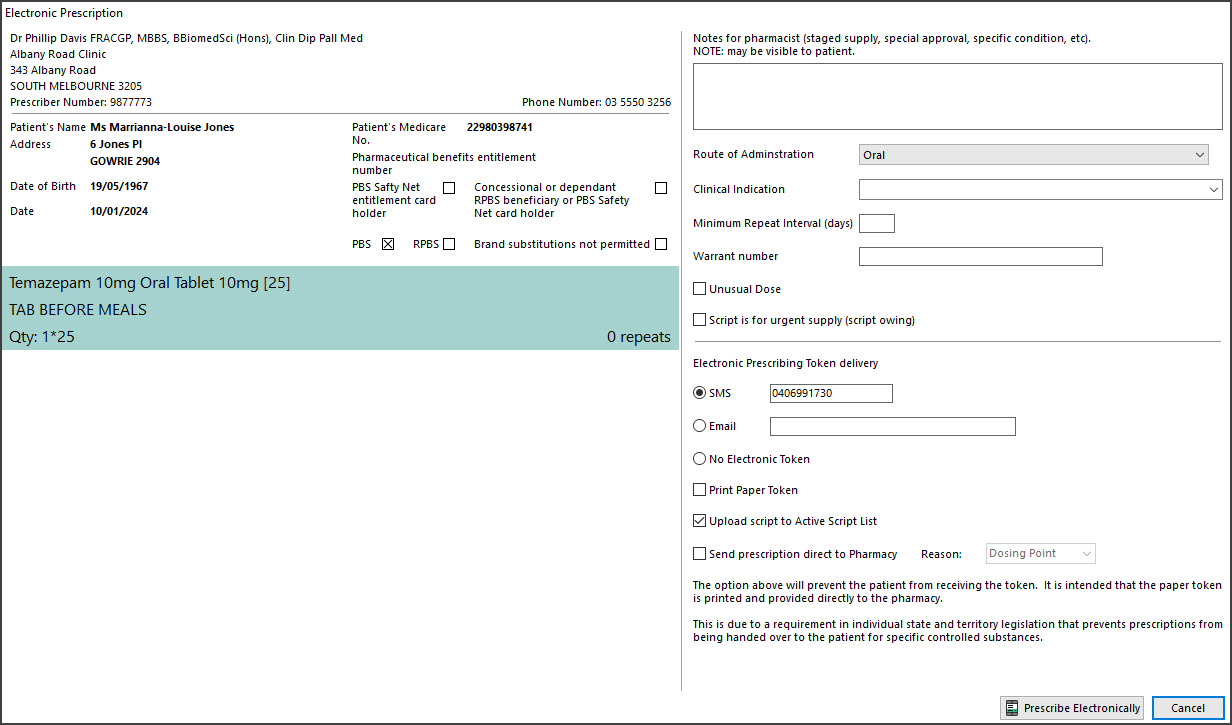
- The prescription has now been created, and the script will appear in the Today's Scripts field.
If a mistake is made, you can right-click the script and select Cancel.
Select Close to exit the prescribing screen.
Link the prescription to a specific problem (optional)
If more than one problem has been entered during the encounter, you can link the prescription to a specific problem. To do this, right-click the Drug in the Today's Scripts field then select Change Problem > Name of problem./li>ePrescribing repeat scripts
An electronic prescription token contains authorisation for repeats as specified by the doctor. Pharmacies manage these repeats for the patient and can provide one repeat token at a time. When a patient goes to the pharmacy, the pharmacist will provide the token for the repeat and ask the patient how they want the token to be provided: SMS or printed. When a patient returns for a repeat script, the next token will be released. If a patient loses a repeat token, the pharmacy can retransmit it if the patient goes to the pharmacy that originally issued it.
Authority approval
When prescribing a drug that can be covered by the PBS with pre-approval, the Approval screen will open when you select Prescribe Electronically or Prescribe. Visit Services Australia to learn more or contact PBS directly.
This screen facilitates your call to the hotline for an approval code and for an Authority-required (STREAMLINED) prescription that does not require prior approval but does require the recording of a streamlined authority code.

Authority approval (Hotline)
Use this process for drugs that do not have Authority Restriction codes. To get an approval code, call the hotline and provide the information requested. All the information you need is on the upper left of the screen.
Authority approval (Streamlined)
Use this process for drugs that have codes in the Authority Restriction field. These drugs do not require prior approval but do require the recording of a streamlined authority code. This code is for the treatment described in the Text to Appear on Prescription field.
- Select the code for the treatment in the Streamline Authority box.
- Select the applicable button:
- Authority to record the code.
- Postal you want to post the approval request to the department. The approval number will be posted back.
Send Directly to Patient sends the authority approval request to the patient, and is for specific drugs where the patient needs to apply directly for authority approval themself. - Defer if you need to do more scripts and want to do their approvals altogether (with 1 call).
- Private if the patient is paying for the prescription themself.
Script details screen (all options)
The Create a prescription section above explains how to use the Script Details screen when prescribing. This section takes a closer look at some of the less-used options in the Script Details screen.
Script Details screen fields:
- Regular Use, PRN, or short-term use of the drug will be selected according to the MIMS default but can be changed.
- Quantity - displays the number of packs, as well as the units per pack (according to MIMS) and is editable.
- Repeats - used to set the number of repeats with the maximum number set by MIMS.
- Script Date - automatically assumes today’s date, and the Medicine estimated to last until (or expiry) and Warn me to renew script after dates will update accordingly. All of these dates can be manually updated, and the Warn me to renew script after option can be enabled either by manually setting the corresponding date or ticking the corresponding checkbox.
- Hide from display (archive) if not current - ticking this means that the drug won’t be readily visible in the patient’s Summary Views when it’s no longer current.
- The PBS Status can be set, between Private, PBS / RPBS, RPBS, PBS, or Section 100
- Regulation 24 (Reg24), and Authority prescriptions - can manually be set, as can the ability to restrict the prescription to one brand (Brand Substitution NOT Permitted) by ticking the corresponding checkbox/s. Brand substation is not available for generic drug selections
- Drug Notes- used to add further information regarding the prescription, which can then also be added to your current encounter by selecting Add to encounter notes.
- MIMS P.I doctor information and MIMS C.M.I patient information documentation is available, except when prescribing generic drugs, by selecting the corresponding button.
- Add to Favourite - adds the prescription to your favourites list with all of the details currently entered. This is useful for a drug that's frequently prescribed for the patient.
- Add to History - adds the prescription details to the patient’s history, regardless of whether it’s actually prescribed during this encounter. This is used to enter any medications the patient is taking that were not prescribed by the doctor.






 Clicking the banner opens the RTPM portal so you can log in to look up the patient and perform a script history check. The portal will be SafeScript in
Clicking the banner opens the RTPM portal so you can log in to look up the patient and perform a script history check. The portal will be SafeScript in 


 Select the script then the Print Scripts icon to print it out.
Select the script then the Print Scripts icon to print it out.

 b) Review the fields on the Electronic Prescription screen.
b) Review the fields on the Electronic Prescription screen.

